Warehouse Management System (WMS): What It Is and How It Is Utilized
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a sophisticated software application designed to optimize the daily operations of a warehouse. From inventory management to order fulfillment, a WMS plays a critical role in ensuring that warehouse activities are streamlined, efficient, and accurate. Let’s delve into what a WMS is and how it is utilized in modern logistics and supply chain management.
What Is a Warehouse Management System?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software solution that provides visibility into a company’s entire inventory and manages supply chain fulfillment operations from the distribution center to the store shelf. The primary functions of a WMS include tracking inventory levels, managing warehouse space, and facilitating the picking, packing, and shipping of orders.
Key features of a WMS include:
- Inventory Management: Real-time tracking of inventory levels, locations, and movements within the warehouse.
- Order Management: Efficient processing of orders, ensuring that items are correctly picked, packed, and shipped.
- Space Utilization: Optimizing the layout and space within the warehouse to maximize efficiency and storage capacity.
- Labor Management: Monitoring and managing warehouse staff productivity and workflows.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights and data analysis to improve warehouse operations and decision-making.
How Is a Warehouse Management System Utilized?
A WMS is implemented to enhance various aspects of warehouse operations. Here are some key ways in which it is utilized:
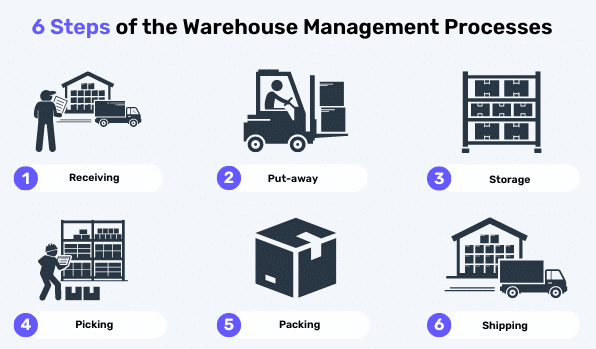
1. Receiving and Putaway
When new stock arrives, the WMS helps streamline the receiving process by verifying quantities, inspecting for damages, and updating inventory records. Once items are received, the system directs warehouse staff on where to store them, optimizing space and ensuring items are easy to locate when needed.
2. Inventory Management
A WMS provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, helping prevent stockouts and overstock situations. It keeps track of every item in the warehouse, including its location and movement history, allowing for accurate and efficient inventory management.
3. Order Fulfillment
When an order is placed, the WMS coordinates the picking, packing, and shipping processes. It generates pick lists for warehouse staff, ensuring that items are picked in the most efficient manner. The system also verifies that the correct items are packed and prepares shipping labels and documentation.
4. Shipping
The WMS manages the shipping process by integrating with carriers to ensure timely and accurate deliveries. It tracks shipments, provides real-time status updates, and manages documentation to streamline the shipping process.
5. Returns Management
Handling returns efficiently is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction. A WMS manages the returns process by updating inventory records, inspecting returned items, and ensuring they are restocked or processed accordingly.
6. Analytics and Reporting
By collecting and analyzing data on warehouse operations, a WMS provides valuable insights that can be used to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. Detailed reports on inventory levels, order accuracy, and labor productivity help warehouse managers make informed decisions.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, a Warehouse Management System is an indispensable tool for any organization involved in logistics and supply chain management. By providing real-time visibility, improving accuracy, and enhancing efficiency, a WMS helps businesses streamline their warehouse operations and achieve greater operational success. Implementing a WMS can lead to significant improvements in inventory management, order fulfillment, and overall warehouse productivity, making it a critical component of modern warehouse management.